- 29/03/2025
- Kaizen Gastro Care
- 0 Comments
- Proctology
Pilonidal Cyst: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
A pilonidal cyst is a common but often misunderstood medical condition that affects thousands of people worldwide. This condition appears at the base of the tailbone and can lead to significant discomfort and complications if left untreated. Dr. Samrat Jankar, a leading expert in colorectal surgery in Pune at Kaizen Gastro Care Clinic, provides comprehensive care for pilonidal cysts, ensuring the best possible outcomes for his patients. His expertise and patient-centered approach make him a trusted choice for those suffering from pilonidal cysts.
In this blog, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pilonidal cysts.
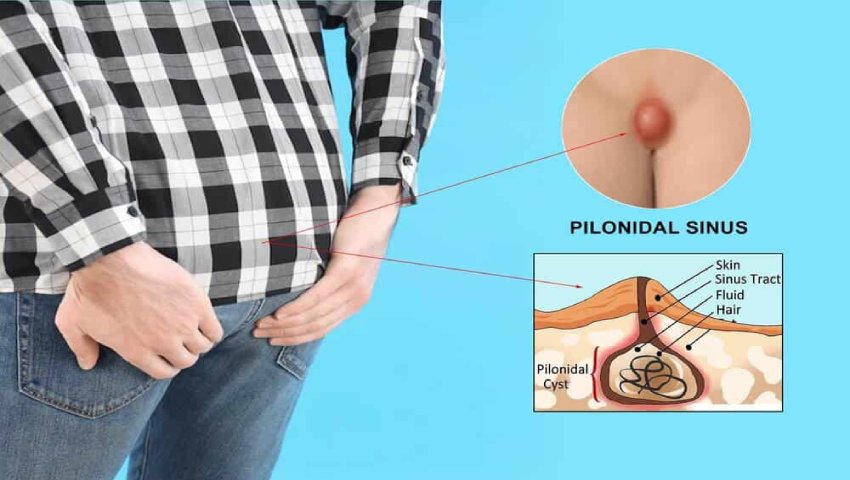
What is a Pilonidal Cyst?
A pilonidal cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the crease of the buttocks, near the tailbone. It usually contains hair, skin debris, and other materials. These cysts form due to hair penetration into the skin, causing an inflammatory response. If infected, a pilonidal cyst can lead to the formation of an abscess, resulting in severe pain and discomfort.
Causes of Pilonidal Cyst:
The exact cause of pilonidal cysts is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to their development:
- Ingrown Hair – One of the leading causes of pilonidal cysts is the penetration of hair into the skin. The body responds to the hair as a foreign object, leading to inflammation and cyst formation.
- Friction and Pressure – Sitting for prolonged periods, particularly on hard surfaces, can put pressure on the coccyx area, improving the risk of developing a cyst.
- Hormonal Changes – Pilonidal cysts are more common in young adults, likely due to increased hair growth and oil production during puberty.
- Poor Hygiene – Accumulation of sweat and dirt in the area can contribute to bacterial infections, leading to cyst formation.
- Obesity – Excess body weight increases the pressure on the lower back and buttocks, which can cause hair to penetrate the skin more easily.
- Family History – Genetic factors may play a role in the susceptibility to pilonidal cysts.
Symptoms of Pilonidal Cyst:
Symptoms of a pilonidal cyst vary depending on whether the cyst is infected or not. Common symptoms include:
- Pain and Tenderness – Discomfort in the lower back or near the tailbone, which worsens when sitting.
- Swelling and Redness – The affected area may appear swollen, inflamed, and tender to the touch.
- Pus or Blood Drainage – Infected cysts may ooze foul-smelling pus or blood.
- Formation of Abscess – If the cyst becomes severely infected, an abscess can develop, leading to increased pain and fever.
- Recurring Cysts – Some individuals experience recurrent pilonidal cysts even after initial treatment.
If left untreated, an infected pilonidal cyst can develop into an abscess, leading to more severe complications.
Diagnosis of Pilonidal Cyst:
Diagnosing a pilonidal cyst is usually straightforward. Dr. Samrat Jankar performs a physical examination of the affected area, assessing swelling, redness, and drainage. In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be advised to evaluate the extent of infection or abscess formation.
Treatment Options for Pilonidal Cyst:
Treatment for pilonidal cysts depends on the severity of the condition. Options range from conventional management to surgical intervention.
Conservative Treatment:
For mild or non-infected cysts, conservative measures may help manage symptoms:
- Warm Compresses – Applying warm compresses can help decrease inflammation and discomfort.
- Good Hygiene – Keeping the area clean and dry can prevent bacterial infections.
- Shaving the Area – Regular hair removal can reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Antibiotics – In cases of mild infection, oral antibiotics may be prescribed.
Drainage of Abscess:
If the cyst becomes infected and forms an abscess, drainage may be required. This involves:
- Incision and Drainage (I&D) – A minor surgical procedure where the abscess is opened, and pus is drained.
- Dressing Changes – Regular wound care is necessary to stimulate healing and prevent reinfection.
Surgical Excision:
For recurrent or severe pilonidal cysts, surgical removal is often the best option. Common procedures include:
- Wide Excision – The cyst and surrounding tissue are completely removed, leaving an open wound that heals over time.
- Marsupialization – The wound edges are stitched down to create a pouch, reducing healing time.
- Flap Surgery – A more advanced approach where nearby healthy tissue is used to close the wound, minimizing recurrence.
Post-Surgical Care and Prevention:
After surgery, proper wound care is important to prevent complications. Patients should:
- Keep the area clean and dry.
- Avoid prolonged sitting and pressure on the wound.
- Follow a hair removal regimen to prevent recurrence.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing to decrease friction.
- Maintain a healthy weight and practice good hygiene.
Conclusion:
A pilonidal cyst can be a painful and recurring condition if not treated properly. Early diagnosis and the right treatment approach can help prevent complications and enhance the quality of life. If you experience symptoms of a pilonidal cyst, consult Dr. Samrat Jankar at Kaizen Gastro Care Clinic for expert advice and effective pilonidal cyst treatment in Pune.
Book an Appointment Today!
If you or a loved one is struggling with a pilonidal cyst, don’t wait for complications to arise. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Samrat Jankar at Kaizen Gastro Care Clinic and take the first step toward relief and recovery.
